
How I understand the Blockchain | Simplified for the Nontechnical
What is a blockchain?
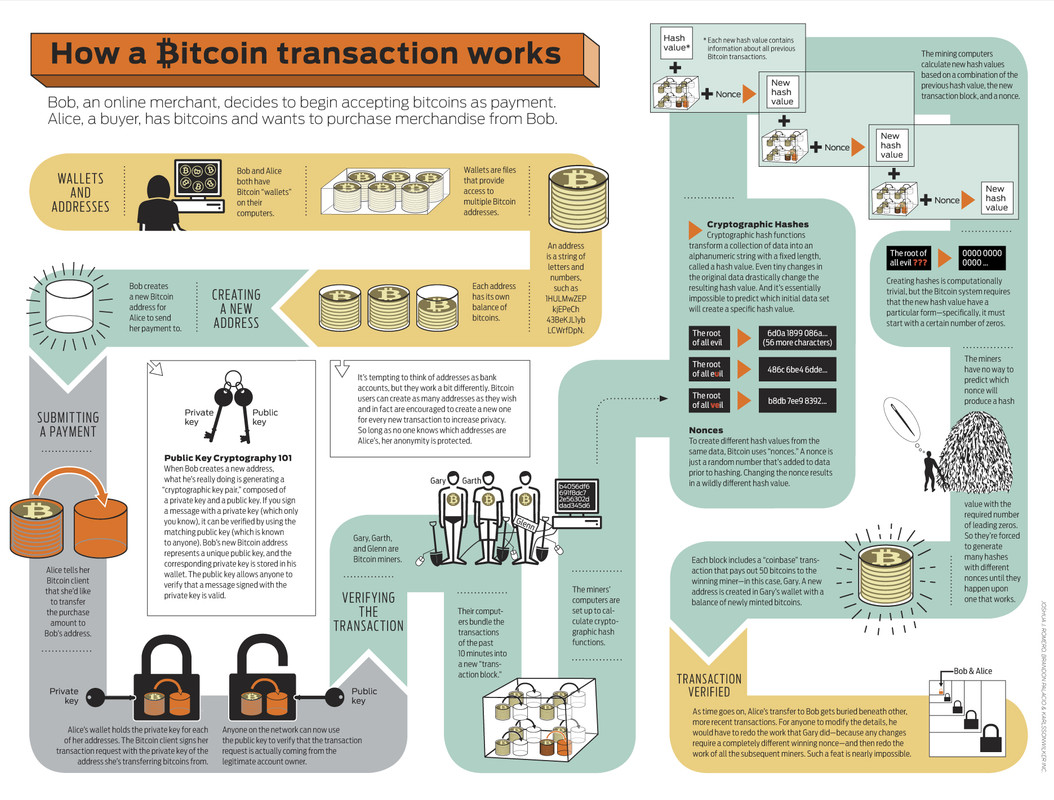
A blockchain is a technology that allows anyone to make instantaneous transaction on the internet without a middleman.
How does a blockchain work? Imagine a secured chain of blocks that contains digital information and are connected to each other. These digital information are actually records of transactions that are similar to what a ledger is, and anyone who uses the blockchain can make and validate these online transactions.
Let us say you purchased an apple from Peter's Farm. Because you used the blockchain to make the transaction, then the blockchain will record your purchase as "You bought an apple from Peter's Farm for $1." Since there are other customers, store owners and farmers who are also using the same blockchain, the purchase you made will be automatically broadcasted to all the members of this network. This means that everyone can also testify to the validity of the transaction, that is, if the purchase made was in agreement to the rules which were previously defined by the network of customers, store owners and farmers. Of course, if there was a mistake on the record, example the record says that you bought an apple from Sally's farm instead of Peter's, then the blockchain will reject the transaction as it does not sync up with the rules defined by the network. This democratic system is the biggest reason for why most people are flocking to using the blockchain technology.
The Blockchain is Decentralized. There is no governing body or central authority that manages the transactions in the blockchain. What does this mean? Let me illustrate.
Let us say that you live in an apartment, and every end of the month, you pay your landlord rent. So you write your landlord a check, the landlord deposits the check to a bank, the bank processes the check and this may take a few days as the bank will need to verify that all the information is correct, and finally, the landlord received the rent money. Now, if you're paying using a blockchain-based currency, then the transaction is just between you and your landlord. All you need to do is to pay the landlord.
Can someone hack the blockchain?
Because of the algorithm that's used on the blockchain, and since there are multitudes of computers that validate and revalidate the transaction on the network, hacking the system can be extremely difficult and tedious.
Who uses the blockchain?
Financial institutions are using the blockchain to cut the middleman and to make banking transactions faster and more effective. The fewer the steps on the transaction the lesser the risk. Digital Content Distributors would use the blockchain to prevent piracy. In the medical industry, the blockchain is used to support the supply chain and prevent theft or transaction fraud. Farmers and the food industry use the blockchain to monitor their crop and supply inventory. The retail industry uses the blockchain to reward loyal customers. And this list of blockchain users is growing.
What are Popular Examples of Blockchain Currencies?
Bitcoin (BTC) - This is the most popular cryptocurrency that is built on the blockchain. Most cryptocoins are traded against the bitcoin and so it's price in the market can tremendously affect the price fluctuations of the coins that are traded against it. Trading your BTC for your local currency can be done via all Crypto Currency exchanges. The most popular of which is Binance.
Ethereum (ETH) - This is the second most popular cryptocurrency, and just like your bitcoin, it too can be mined, traded using Binance, and sent to anyone in world instantly via the Ethereum blockchain network. But that is not the only thing it can do, in Ethereum you can also build decentralized application or Dapps that can be controlled or programmed to doing specialized transactions called contracts. The Ethereum blockchain community remains to be the largest and most active blockchain community in the world.
Steem (STEEM) - Steem is a cryptocurrency that is based on a blockchain that is focused on social interactions and content development. Think of Facebook, Twitter, Youtube and Instagram on a decentralized platform. All of these popular social media organizations have an equivalent application that is powered by the Steem blockchain. The only difference is that when you use these Dapps, you are rewarded for creating, sharing and liking the uploaded digital contents.
That's it. Hopefully you now have a firm grasp of what a blockchain is and is also familiar with some of its more popular examples.









Comments